What is DeFi? A Simple Guide to Decentralized Finance 2025

Decentralized finance (DeFi) is an emerging financial technology based on secure distributed ledgers similar to those used by cryptocurrencies.
Today, people are asking about DeFi because it promises an alternative to the traditional banking system, offering new ways to trade, lend, and manage money without a middleman. This guide breaks down exactly what DeFi is, how it works, and how you can get started.
What Is DeFi (Decentralized Finance)?
DeFi, which stands for Decentralized Finance, is a new kind of financial system built on blockchain technology. So, think of it like this: instead of a bank or a company holding your money and managing your transactions, all of that is handled by a public, open network. Here, the main goal of DeFi is to get rid of the middleman.
A good way to understand this is to use a real-world analogy. So, imagine you want to lend money. In the old system, you might go through a bank, and the bank would check both of your credit scores, set the terms of the loan, and take a fee for its services. That’s the entire process.
Now, in a DeFi system, you could lend money directly using an automated contract. This contract would have all the rules of the loan built into it, like the interest rate and repayment schedule. The code would make sure everything happens automatically and fairly, so neither of you needs a bank to handle it. You know, this system runs on a blockchain, so all the transactions are recorded and transparent for everyone to see.
This DeFi definition means you have full control over your money, and you can access financial services from anywhere in the world, 24/7, just with an internet connection. Hence, it is an open and transparent alternative to traditional finance.
DeFi vs. CeFi (Comparison Table)
| Aspect | CeFi (Centralized Finance) | DeFi (Decentralized Finance) |
| Custody | A bank or exchange holds your deposits and handles security on your behalf | You hold your own keys and manage funds in a wallet you control |
| Permission/KYC | Accounts require identification (KYC) and approval from a regulated company | Anybody with internet access can interact; no account approval is needed |
| Settlement | Transfers may take days as they go through clearing houses and intermediaries | Smart contracts settle transactions almost instantly on the blockchain |
| Fees | Banks and brokers charge service and transaction fees | Users pay gas fees to miners/validators to process transactions |
| Failure/Recourse | Regulators and insurance may reimburse you in case of fraud or bankruptcy | Bugs or hacks can result in permanent loss; recovery depends on the community and code fixes |
| Dispute handling | There is a legal process to resolve disputes or errors | Disputes are tough to handle since code executes automatically |
So, yes, DeFi offers a compelling vision of open, permissionless finance, but it’s important for you to know that CeFi isn’t going away anytime soon. You know, centralized exchanges like Binance or Coinbase, and financial institutions still provide services that many people rely on, like customer support, insurance on deposits, and easy-to-use platforms.
Also, they act as a bridge for many newcomers to crypto. DeFi’s technical complexity and risks, such as smart contract bugs and a lack of recourse, mean it doesn’t instantly “replace banks” or traditional finance, but instead, both systems are likely to coexist and serve different user needs.
How DeFi Works?
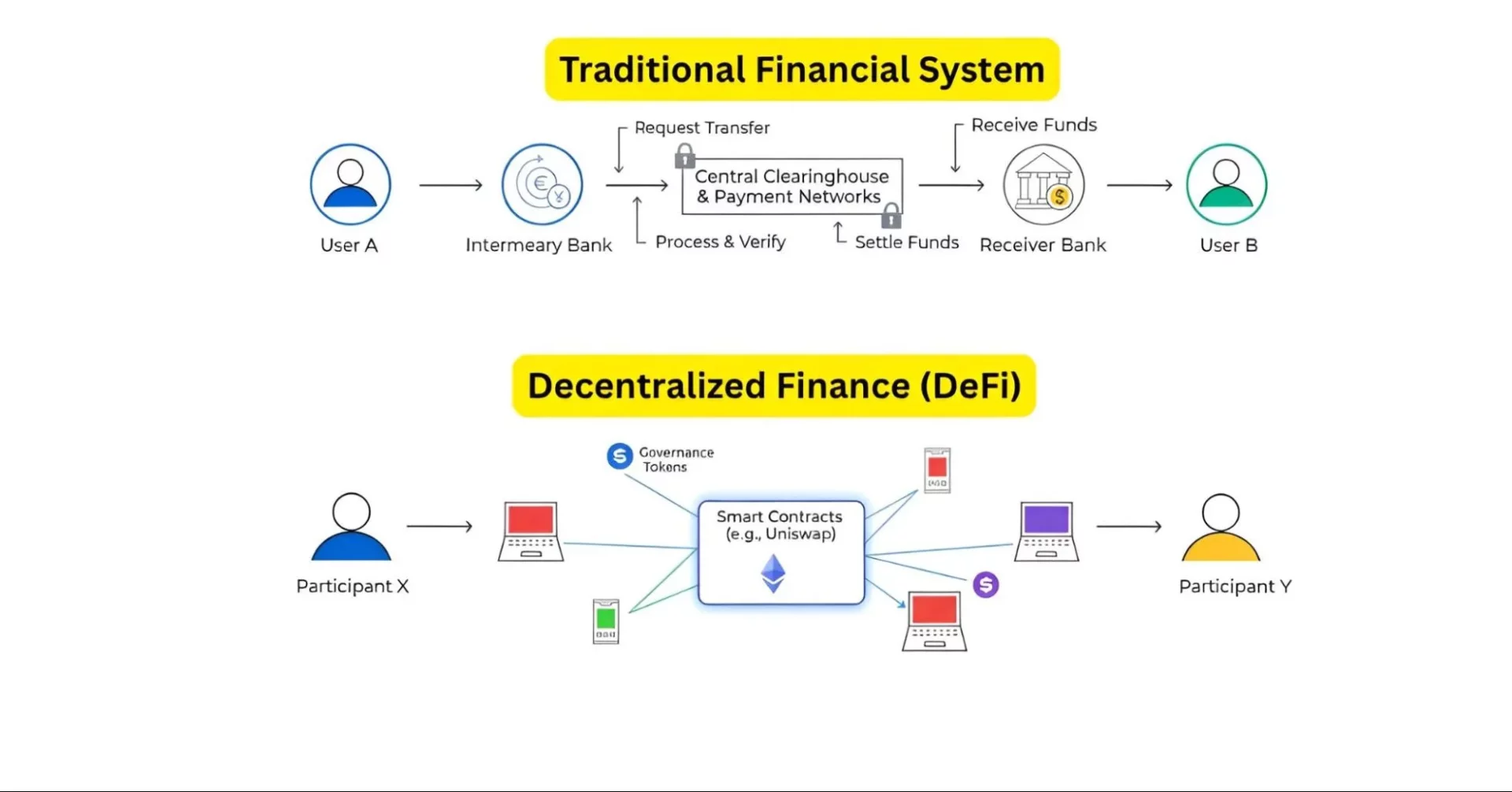
DeFi works by using blockchain technology to create a financial system that’s open and available to everyone, without the need for traditional banks or other financial companies. It allows you to use financial services like lending, borrowing, and trading directly with other people using code.
Now, to know exactly how DeFi works, you need to understand its main components.
- Smart Contracts: The most important part of DeFi is the smart contract. These are just lines of computer code that run on the blockchain, and they have rules built into them. Hence, they execute automatically when those rules are met. For example, a smart contract can be set up to automatically swap one type of token for another once a trade request is made. Basically, this removes the need for a third party to process those transactions.
- Web3 Wallet: Your journey into DeFi starts with a Web3 wallet. It’s basically your personal tool for accessing everything in the DeFi world. You can use this wallet to hold your cryptocurrencies and to connect to different DeFi applications.
- Tokens & Gas Fees: All your money in the DeFi system is in the form of digital assets, or tokens. There are all kinds of tokens, but one of the most useful kinds is a stablecoin. A stablecoin is a cryptocurrency whose value is tied to a real-world asset, like the US dollar. Hence, this helps make transactions more predictable since stablecoins don’t have the crazy price swings that other cryptocurrencies can have. Also, as DeFi explained above, when you make a transaction, you have to pay a small fee, and this is called a gas fee. It’s generally what you pay to the network to process and secure your transaction.
What Can You Do With DeFi?
You can do things with DeFi like using decentralized exchanges (DEXs) to trade cryptocurrencies, lending & borrowing digital assets, earning rewards through staking & yield farming, and using stablecoins & payments for transactions.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
A Decentralized Exchange (DEX) is a platform for trading cryptocurrencies. Unlike a traditional, or centralized, exchange (like Coinbase), a DEX doesn’t hold your funds for you. You trade directly from your own wallet, and this really makes it more secure in some ways because you control your private keys and funds at all times.
On a DEX, you don’t trade with other traders’ orders in a list, but instead, you trade with a pool of tokens. This is called a liquidity pool. The liquidity pool is controlled by a smart contract, so when you want to trade one token for another, for example, ETH for DAI, you send your ETH to the smart contract, and the smart contract sends you the equivalent amount of DAI from the pool. This process is called a “swap”.
Here, the liquidity in these pools comes from other users called Liquidity Providers (LPs). These LPs are people who deposit a pair of tokens into a liquidity pool to earn some rewards. Mostly, DEXs share trading fees with LPs. Well, Uniswap is one of the most well-known DEXs, and it is a good example of how a DEX works. It operates on the Ethereum blockchain.
Lending & Borrowing
DeFi lending and borrowing let people lend out their crypto to earn interest or borrow more cryptocurrency by providing collateral. And it’s all done using smart contracts, without a bank in the middle.
Now, since there is actually no credit check here, borrowers must put up more value in crypto than they are borrowing. This is called over-collateralization. So, for example, you might need to deposit $150 worth of Ether to borrow $100 worth of stablecoins. Mainly, this extra collateral is there to protect the lender in case the value of your collateral goes down.
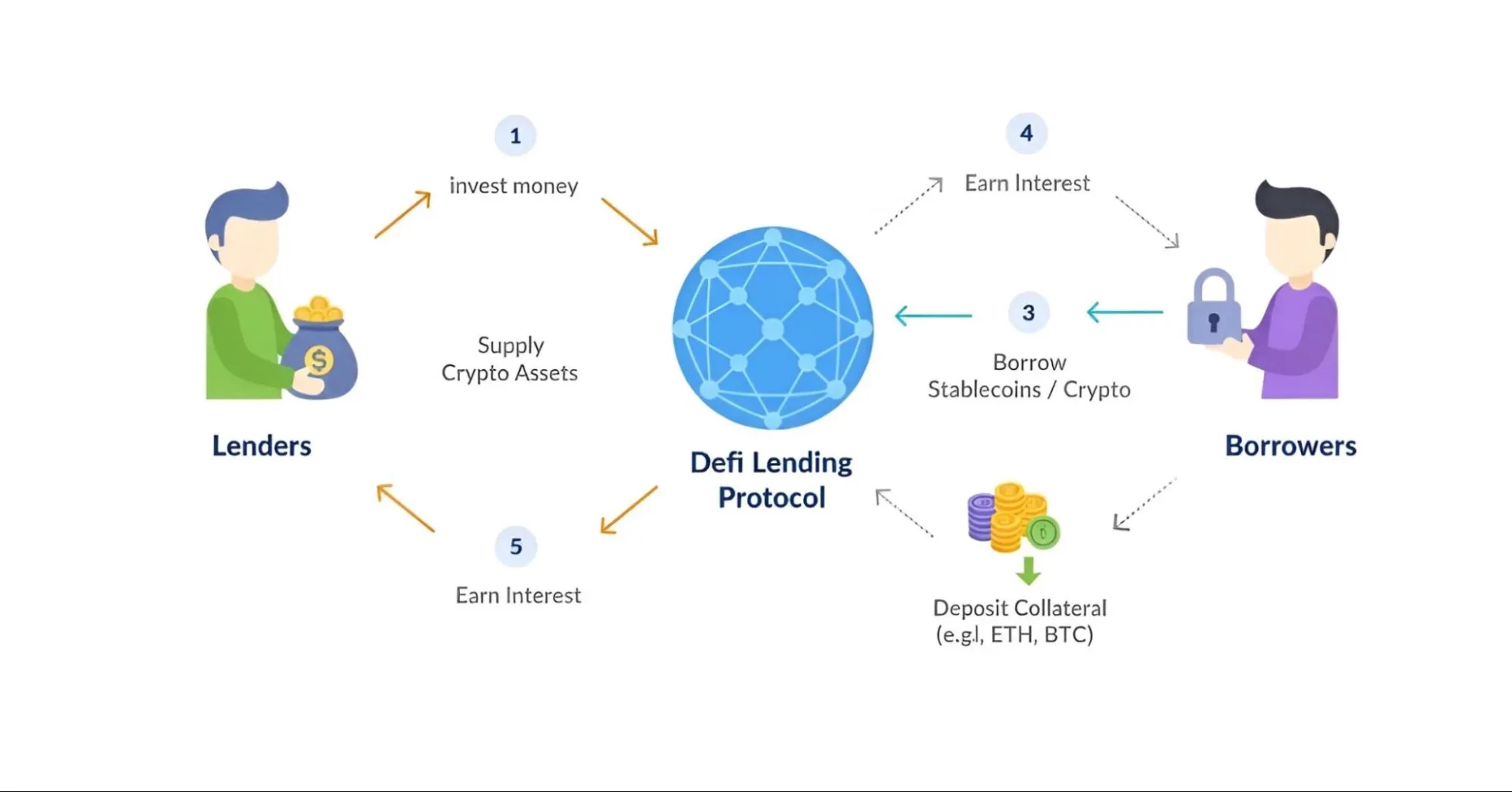
Aave is a major DeFi lending platform, and it uses a system of liquidity pools. So, lenders deposit their crypto into a pool, and borrowers take crypto from the same pool. The interest rates are not fixed; they change based on how much supply and demand there is for a particular crypto in the pool. Also, MakerDAO is another important protocol. It lets users use a stablecoin called DAI.
Well, DeFi is good, but there are certain risks involved with the lending and borrowing part. The main one is liquidation. So, if the value of your collateral drops too much and it’s not enough to cover your loan, your collateral can be automatically sold off by the smart contract to pay back the loan.
Another one is related to oracles. An oracle is a service that brings real-world data, like the price of a crypto, to the blockchain, and if an oracle gives the wrong information, a smart contract might make a mistake, like liquidating a loan when it shouldn’t be.
Staking & Yield
Staking in crypto is a way to earn rewards for holding and securing a blockchain. To be exact, it is mostly for blockchains that use a “Proof of Stake” system. You can lock up your coins, and in return, you get to help validate transactions and secure the network. Now, for this work, the network pays you with new coins as a reward. This whole process is a way to earn a yield on your crypto, and it’s a bit like earning interest in a savings account. If you are looking for top-earning sites, you can read our guide on the best crypto staking platforms.
Yield farming is a more complex way to earn yield compared to crypto staking. It involves moving your crypto assets around different DeFi protocols to get the best returns. So, for example, you can deposit your tokens into a lending protocol to earn interest, or you might provide liquidity to a DEX to earn trading fees.
The thing is, yield farmers try to find the most profitable opportunities at any given moment. Well, this can also involve risk, because moving assets between different protocols can expose you to more smart contract risks. Here, the yield can come from different sources, such as fees, interest, or rewards paid in the protocol’s native token.
Stablecoins & Payments
Stablecoins are a type of cryptocurrency that is designed to have a stable value. Usually, they are tied to a real-world asset, like the US dollar. So, one stablecoin might always be worth one US dollar. Hence, this stable value makes them useful for payments and trading because they don’t have the price swings that other cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin have.
You can easily use stablecoins for payments, like for sending money abroad (remittances), and this is a big advantage. You know, traditional international transfers can be slow and expensive. Stablecoins, since they are on a blockchain, can be sent almost instantly, 24/7, and even with very minimal fees. Hence, this makes it much easier to send money to different countries. Also, on-chain payments just mean the payment is happening directly on the blockchain, and it is recorded there forever. This makes the payments transparent and very easy to verify.
But of course, there are certain risks. The main risk with stablecoins is the peg risk. Mainly, this is the risk that the stablecoin might lose its stable value and not be worth what it is supposed to be. So, let’s say, a stablecoin that should be worth $1 might drop to $0.90. This can happen for different reasons.
For stablecoins backed by fiat money, the risk is that the company holding the money does not have enough reserves. And for stablecoins that use other cryptocurrencies as backing, like MakerDAO’s DAI, the risk is that the value of the collateral drops too much, or the smart contract has a problem. For algorithmic stablecoins, which use smart contract code to manage their supply and value, the risk is that the algorithm fails. Eventually, if a stablecoin loses its peg, it can cause big losses for the people who hold it.
Benefits & Risks of DeFi
The benefits of using DeFi are open access, transparency, control over assets, lower costs, innovation and yield opportunities, and programmable money.
The risks of using DeFi are smart contract bugs, market volatility, regulatory uncertainty, phishing and scams, stablecoin dependency, and complexity & user error.
Benefits
- Open Access: DeFi applications are open to anyone with an internet connection and a compatible wallet. You do not need to fill out paperwork or live in a certain country. Hence, this openness brings financial transactions to people in regions where traditional banking services are limited.
- Transparency: Every transaction and program rule is recorded on a public blockchain, and this level of transparency easily lets users audit the code and transaction history. There are no hidden fees or secret changes to the rules, and even if a problem arises, the community can trace exactly what went wrong.
- Control Over Assets: Since you hold your private keys, you decide when to move your funds. Here, banks do not have the authority to freeze your account or limit your withdrawal.
- Lower Costs: You know, there are no middlemen, so without intermediaries, fees are often lower. Sending a stablecoin can cost pennies or a few dollars compared to bank wires, which can easily cost twenty to fifty dollars. Also, trading on DEXs typically incurs small percentages taken from each swap, and those fees return to liquidity providers.
- Innovation and Yield Opportunities: DeFi platforms compete to attract users, so they often offer yields higher than a traditional savings account. And, you can actually earn rewards by providing liquidity, staking, or farming tokens.
- Programmable Money: Developers can build complex products like insurance, derivatives, and prediction markets directly on the blockchain. And since everything runs on code, new features can roll out quickly without waiting for approval from a corporate board or government agency.
Risks
- Smart Contract Bugs: Code can contain errors, and even with careful audits, bugs have allowed attackers to drain funds from DeFi protocols from time to time. There is usually no recourse once funds are stolen.
- Market Volatility: You know, cryptocurrencies can swing up or down very quickly, and if you take a loan and the value of your collateral plummets, you could be liquidated and lose a portion of your assets.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Laws around DeFi are still forming. Governments may require identification from you for certain transactions or even restrict access to some services. Also, tax treatment can vary, so staying aware of local laws and following updates is important.
- Phishing and Scams: Since you control your wallet funds, scammers target you directly. Fake websites, malicious links, and impostor support agents aim to trick you into revealing your seed phrase or approving a bad contract.
- Stablecoin Dependency: Many DeFi activities revolve around stablecoins, and if a major stablecoin loses its peg or collapses, it could cause chaos across multiple platforms. Also, in the past, some algorithmic stablecoins have failed before when market conditions turned against them.
- Complexity & User Error: DeFi interfaces can be confusing for newcomers. Hence, simple mistakes like sending tokens to the wrong address or approving unlimited spending can easily lead to loss. To avoid such errors, you need to use user-friendly wallets, so check out our guide on the best crypto wallets.
How to Get Started with DeFi?
To get started with DeFi, you need to get a non-custodial wallet, fund it and choose a network, try a small first transaction, manage approvals, and practice risk management.
Step 1: Get a Non-Custodial Wallet
First, you need to download a non-custodial wallet. This type of wallet is critical because it allows you complete control over your private keys and, as a result, your money. Unlike having a crypto exchange hold your money for you, with a non-custodial wallet, you become your own bank. Some of the best crypto wallets are MetaMask, Trust Wallet, and Coinbase Wallet.
Now, once you install the wallet, you can create a seed phrase of 12 or 24 words. You have to write it down and keep it offline in a secure place. In case you lose your wallet or your device gets damaged, this phrase is the only way to get your money back. Also, for a large sum of money, we suggest you get a hardware wallet as it will keep your keys offline and make them much more difficult to steal.
Pro tip: Never store your seed phrase in an email or on cloud storage. You should use a physical notebook or a metal plate to prevent digital theft.
Step 2: Fund Your Wallet and Select a Network
Next, you must fund your crypto wallet with some digital currency. You can accomplish this by purchasing crypto on a standard centralized exchange such as Coinbase or Binance and then transferring it to your new wallet address. You must select a network when you send it. Ethereum is the primary network to use for DeFi, but its fees are often a little high.
For a new user, it may be preferable to begin on a Layer 2 (L2) network such as Arbitrum or Optimism, which are based on Ethereum but are much cheaper. This allows you to use DeFi without incurring too many fees.
Pro tip: Always look at the gas fees before making a transaction, particularly on Ethereum.
Step 3: Make a Small First Transaction
After your wallet is funded, you should begin with an extremely small transaction. This may be as basic as exchanging one token for another on a decentralized exchange (DEX) such as Uniswap.
This initial small transaction will familiarize you with how the process works. When you make an exchange, you may also notice something referred to as slippage. Well, this is the difference between the price you expect to receive and what you actually receive. You also have to confirm the token you are exchanging, which authorizes the smart contract to use your money to make the trade.
Step 4: Manage Your Token Approvals
When you open a DeFi app for the first time, you will usually be prompted to provide it with a token approval. This is an authorization that allows the smart contract to take your tokens in order to perform activities such as trading or lending.
The danger is that if you are hacked or the smart contract has a flaw, a hacker can use that authorization to drain all of your tokens. It is a good practice to control these authorizations and revoke them once you no longer require them.
Pro tip: Limit approvals only to the amount you intend to use, not to unlimited amounts.
Step 5: Practice Risk Management
As discussed above, DeFi is risky. You might lose your funds due to smart contract bugs, hacks, or simply poor market conditions. One good practice to minimize this risk is to diversify your investments across multiple platforms.
Also, be cautious of projects with extremely high annual percentage yields (APYs) since they tend to be highly risky. As a beginner, it might be a good idea to utilize a separate burner wallet containing little capital to try out new or risky protocols. That way, in case something goes wrong, your primary wallet remains intact.
FAQs
Is DeFi safe/legit?
Yes, DeFi is legit and legitimate, but it is not without risks. Its legitimacy comes from being built on transparent, decentralized blockchains. However, since it operates without central authorities or government regulation, you are generally exposed to risks like smart contract bugs, hacks, and potential scams. Also, there are no built-in consumer protections, so if something goes wrong, you are on your own.
What is an example of DeFi?
A great example of DeFi is Uniswap. Uniswap is a decentralized exchange (DEX) that lets people swap one cryptocurrency for another. So, unlike a traditional stock exchange, there is no company in the middle. The trades are executed automatically by code, using liquidity pools supplied by other users who earn a small fee for providing their assets.
DeFi vs. CeFi: which is better?
Neither DeFi nor CeFi is inherently “better” than the other; they are just different. DeFi is better for users who value decentralization, transparency, and full control over their assets. CeFi, or Centralized Finance, is better for users who prefer simplicity, customer support, and regulatory protections, even if it means giving up some control and privacy. Hence, the real choice depends on your personal needs and risk tolerance.
Do I need Ethereum/L2? What about gas fees?
You do not need Ethereum, but it is the biggest network for DeFi. Most DeFi apps were built on Ethereum first. However, its high gas fees (the cost to perform a transaction) have led to the creation of Layer 2 (L2) networks like Arbitrum and Polygon, which are built on top of Ethereum but are much cheaper and faster. So, while you can use other blockchains, starting on an L2 is a good way to get a feel for DeFi without paying a lot in fees.
Can DeFi replace banks?
DeFi cannot replace banks in its current form, but yes, it offers an alternative for services like lending and borrowing. It lacks many crucial elements of traditional banking, such as deposit insurance, customer service, and legal recourse. Also, DeFi is still a niche technology that appeals to a specific audience, and it has a lot of growth and maturity needed before it can be considered a full replacement for the traditional financial system.
How do DeFi apps make money?
DeFi apps make money primarily through transaction fees. Now, when you use a DeFi protocol for a service like trading, lending, or borrowing, a small fee is often charged. Then, this fee is distributed among the protocol’s users or a community treasury, rather than being collected by a central company.
What is a DeFi wallet?
A DeFi wallet is a digital tool that lets you store your crypto and interact with DeFi apps. Unlike a wallet on a centralized exchange, a DeFi wallet is non-custodial, which means you, and only you, have full control over your private keys. Hence, it is the essential key to the entire DeFi ecosystem.
Bottom Line
In a nutshell, DeFi is a financial system built on code that offers new opportunities for everyone. It’s a powerful and open alternative to traditional finance, but it also comes with real risks like smart contract failures and scams. So, if you’re interested, the best approach is to start small, do your own research, and continue learning as the space evolves.
The post What is DeFi? A Simple Guide to Decentralized Finance 2025 appeared first on CryptoNinjas.



